How does the system support Take 5 / dynamic risk assessments?
The RM integrated digital system supports all the outcomes delivered by using paper and digital paper approaches for pre-task (e.g. Take 5) and dynamic risk assessments through using task workflows. This approach centres on supporting field staff with tailored workflows that have been developed for and with them and it has multiple other business benefits. A digital workflow approach is both tailored and flexible and its primary purpose is to assist field staff to plan and execute their assigned tasks safely and productively across their workday. This includes adjusting and adapting as things change e.g. identifying additional critical risks and new hazards and confirming that required controls are in place. Overview: • Pretask planning and risk management processes are configured into each workflow in ways that are directly relevant to the activities being undertaken. • This means that field staff do not have to adapt and apply a generic paper format, instead the specific activity related critical risks, hazards and control details are built-in. • Critical risks, hazards and their controls covered in the default EDB configuration include electricity (isolation, MAD, and working live), working at height, vehicle movements, load shifting, off road access, noise, dust, temperature, etc. • Importantly, the workflows also capture work environment variables arising from location, weather, time of day, and interactions with other workgroups, members of the public etc. • Also included is a simple task planning workflow that allows users to identify hazards and confirm that controls are in place before commencing work. This option is used for short-duration and low risk tasks e.g. by planners confirming access for future construction works. If a task is repeated several times then a specific workflow is usually built. Further details: Task specific planning prompts and information are built into workflows to assist field staff identify and control critical risks and hazards across their workday, for example: • Start-of-day workflows assist crews confirm that required equipment and materials are onboard and that vehicles and trailers are fit for use with loads are secured. • As required, a workflow for off-road travel may be used, followed by site set-up, electricity isolation and reenergising, use of cranes, working at heights, lifting, phase checking, and making good the site at the end of the job. Each workflow prompts field staff to systematically consider and control risks and hazards for present for the task or task phase. The workflow is an ongoing good practice reference that supports and captures ‘work as done’ decisions and the status of controls through each task phase across the workday i.e. there is a comprehensive operational log of task planning and hazard control decisions. • Ongoing support for decisions across each task phase through the day differs significantly from typical paper or digital paper JSEA, Take 5s, or equivalent processes. These are usually based on generic forms and once completed are are rarely referenced through the workday. • A digital approach also supports staff to pause and reassess control adequacy and make necessary changes during task execution. • It also makes important references and details of standard work processes available when required. This provides default direction in defined situations. Some examples include Trigger Action Response Plans (TARPs) for pole top rescue, COVID19 responses, and interactions with members of the public. Others include providing immediate access to structured task instructions e.g. when recovering stuck vehicles or making changes to lifting plans because of space restrictions requiring short jacking etc.
Can it handle JSEAs / energy wheel or other structured risk tools?
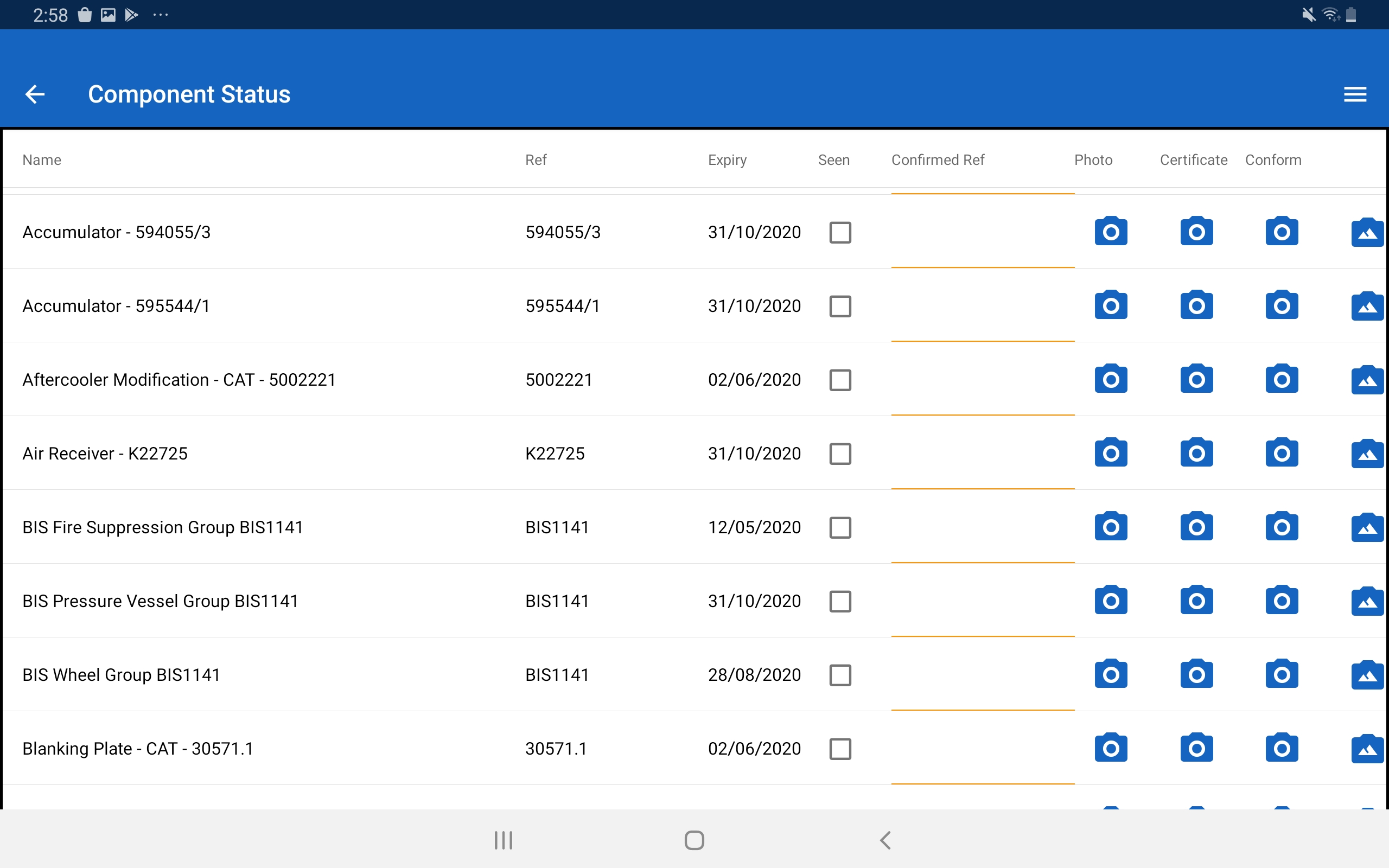
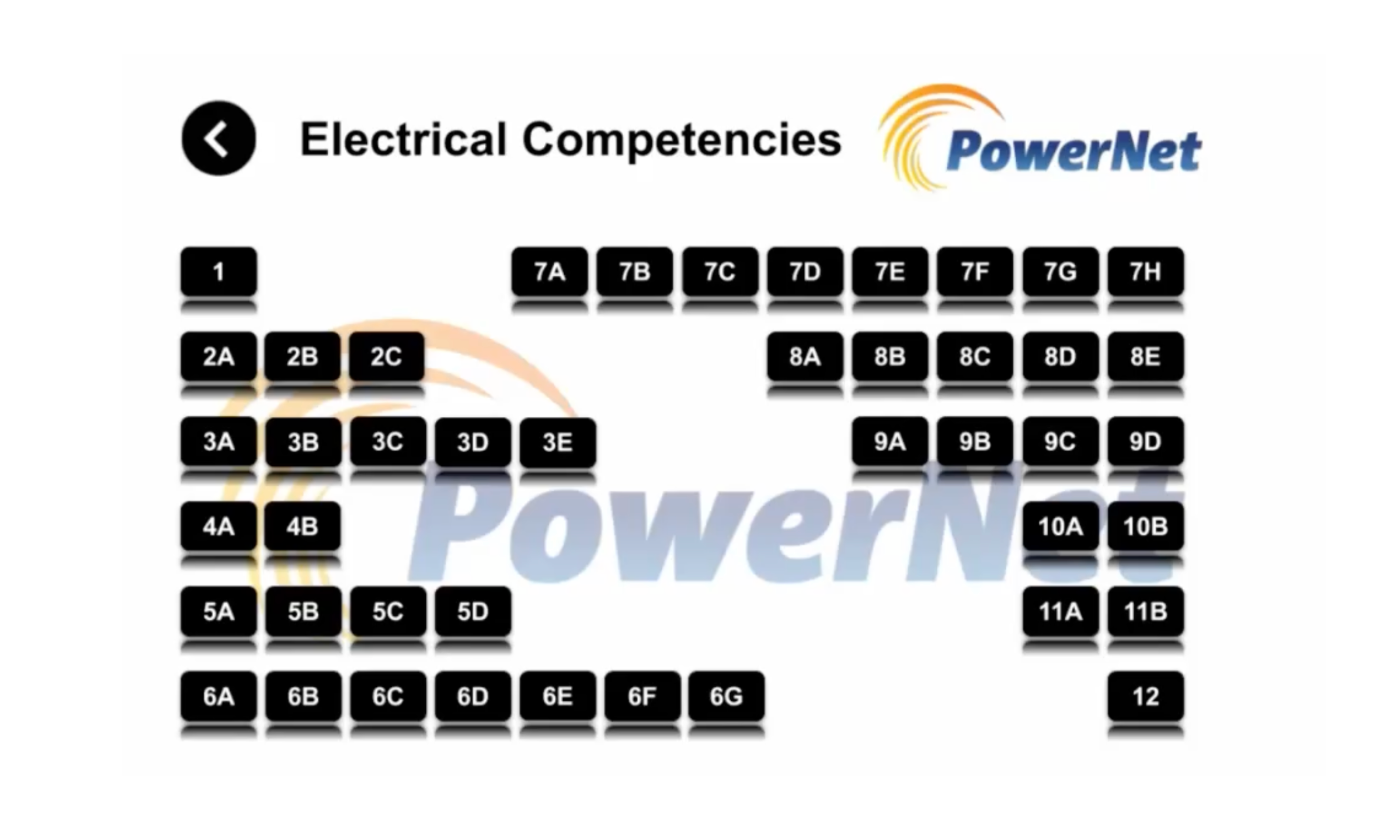
Yes. The RM Form Builder tool allows the addition of graphic information added to digital workflows for field staff. An embedded example is provided on the companion webpage. The application of this approach and others can be field tested during the project pilot phase. Further, once included and identified in task workflows, hazardous energy data points can be used for reporting and analysis e.g. when and how controls are applied and potentially with field staff feedback on control effectiveness. The Energy Wheel graphic or other supporting information can be added to any assessment as a subform with immediate deployment.
How does it link critical risks to controls and verification?
Please note that the PowerNet Critical Control Framework Project Use Case behind the development of the default EDB configured integrated system offered in this proposal, was to improve the management of critical risks, along with streamlining of health and safety management systems for field use. Information on the management of critical risks is derived directly from the use of Field Portal digital workflows. Importantly, the workflows were developed with and for Field Staff and are based on their needs. This means that application of controls for critical risks and hazards are operationally integrated across work planning and execution processes. Importantly this information is captured.
Can incidents, near misses, hazards, audits, and compliance tasks all be logged in one place?
Yes. Once the digital infrastructure with a default EDB configuration is deployed, existing digital workflows can be rapidly configured for HEG, and new workflows developed using RM Form Builder tool, as required. Potential approaches relevant to this question are developed below: • RM can rapidly develop and test a workflow, or workflows, that deliver all HEG requirements for incident reporting and management, along with near miss, hazard, and defect reporting • Field audits - RM can build from already deployed senior management observation workflows. • In addition other workflows e.g. for asset inspections can be rapidly developed, prototyped and iterated following this approach: develop the use case, confirm information required, set up bridges to and from other business systems, (or build a new module). • Recording compliance outcomes and processes - through adapting existing workflows or developing new options as required e.g. test dates for equipment through to actively deploying actions plans from systems audits. Notes: • Further options for capturing, sorting, and using data can be developed rapidly depending on the use case. • The Field Portal App already has a built-in action generator that links to an action escalation and status tracking capability in the Digital Systems Model Platform. • There is also a capability to link and group multiple actions as a single project, or by role, function etc.
How does the system ensure workers are trained and competent before work starts? (integration with training/competency records)
The RM integrated digital system supports all the outcomes delivered by using paper and digital paper approaches for pre-task (e.g. Take 5) and dynamic risk assessments through using task workflows. This approach centres on supporting field staff with tailored workflows that have been developed for and with them and it has multiple other business benefits. A digital workflow approach is both tailored and flexible and its primary purpose is to assist field staff to plan and execute their assigned tasks safely and productively across their workday. This includes adjusting and adapting as things change e.g. identifying additional critical risks and new hazards and confirming that required controls are in place. Overview: • Pretask planning and risk management processes are configured into each workflow in ways that are directly relevant to the activities being undertaken. • This means that field staff do not have to adapt and apply a generic paper format, instead the specific activity related critical risks, hazards and control details are built-in. • Critical risks, hazards, and their controls covered in the default EDB configuration include electricity (isolation, MAD, and working live), working at height, vehicle movements, load shifting, off road access, noise, dust, temperature, etc. • Importantly, the workflows also capture work environment variables arising from location, weather, time of day, and interactions with other workgroups, members of the public etc. • Also included is a simple task planning workflow that allows users to identify hazards and confirm that controls are in place before commencing work. This option is used for short-duration and low risk tasks e.g. by planners confirming access for future construction works. If a task is repeated several times then a specific workflow is usually built. Further details: Task specific planning prompts and information are built into workflows to assist field staff identify and control critical risks and hazards across their workday, for example: • Start-of-day workflows assist crews confirm that required equipment and materials are onboard and that vehicles and trailers are fit for use with loads are secured. • As required, a workflow for off-road travel may be used, followed by site set-up, electricity isolation and reenergising, use of cranes, working at heights, lifting, phase checking, and making good the site at the end of the job. Each workflow prompts field staff to systematically consider and control risks and hazards for present for the task or task phase. The workflow is an ongoing good practice reference that supports and captures ‘work as done’ decisions and the status of controls through each task phase across the workday i.e. there is a comprehensive operational log of task planning and hazard control decisions. • Ongoing support for decisions across each task phase through the day differs significantly from typical paper or digital paper JSEA, Take 5s, or equivalent processes. These are usually based on generic forms and once completed are are rarely referenced through the workday. • A digital approach also supports staff to pause and reassess control adequacy and make necessary changes during task execution. • It also makes important references and details of standard work processes available when required. This provides default direction in defined situations. Some examples include Trigger Action Response Plans (TARPs) for pole top rescue, COVID19 responses, and interactions with members of the public. Others include providing immediate access to structured task instructions e.g. when recovering stuck vehicles or making changes to lifting plans because of space restrictions requiring short jacking etc.